A toothache might start as a dull throb or an annoying sensitivity, but if it stems from an infection, it could spiral into a life-threatening situation. Many people don’t realize that untreated tooth infections can lead to severe complications involving the heart, brain, or other vital organs. For most, modern dental care ensures outcomes don’t reach this extreme—but understanding the risks and acting promptly is critical.
This blog explores how long it takes for a tooth infection to become life-threatening, warning signs to watch out for, and why early treatment is non-negotiable.
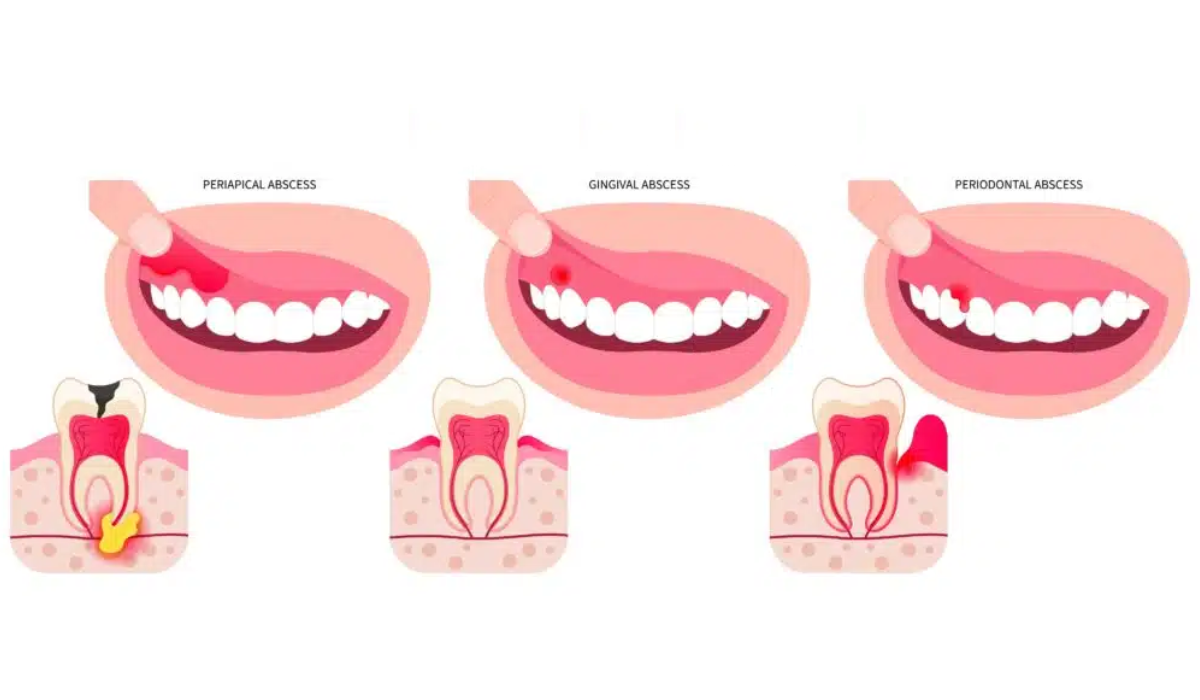
What Is a Tooth Infection?
A tooth infection, also known as a dental abscess, occurs when bacteria enter the tooth’s pulp (the soft center of blood vessels and nerves). This happens due to tooth decay, gum disease, or trauma to the tooth. Once inside, the bacteria multiply, creating a painful collection of pus that can impact the surrounding tissues.
If left untreated, this infection doesn’t stay confined—it can spread to other parts of the body, leading to severe health complications.
Types of Tooth Abscesses:
- Periapical Abscess – Forms at the tip of the root.
- Periodontal Abscess – Occurs in the gums near the tooth root.
- Gingival Abscess – Found in the gum tissue.
How Long Until a Tooth Infection Becomes Dangerous?
The timeline for a tooth infection to turn life-threatening varies. Key factors include the infection’s severity, the individual’s immune response, and how quickly treatment is sought. Here’s a general progression to help you understand the risks more clearly:
Week 1-2:
- Symptoms: Pain around the tooth, sensitivity to hot or cold, and swelling localized to the affected area. These signs might seem manageable but indicate the infection is active.
Week 3-4:
- Abscess Formation: By now, the infection may develop into a noticeable dental abscess. Swelling becomes pronounced, and you might see pus drainage inside your mouth. Systemic symptoms like fever or fatigue could emerge.
Weeks 4-12:
- Progression Beyond the Tooth: Left untreated, bacteria from the abscess could spread beyond the oral cavity. Once the infection reaches other body parts like the jaw, neck, heart, or brain, the risk of life-threatening complications rises significantly. These complications include sepsis, Ludwig’s angina, or a brain abscess.
Days to Death:
When the infection enters the bloodstream or critical areas like the brain, the situation escalates rapidly. Death can occur in as little as one to three days from the onset of severe systemic infection, depending on the individual’s health and the infection’s spread.
Life-Threatening Complications of Tooth Infections
Not all tooth infections result in death, but the risk makes understanding complications essential. Here’s what could happen when an infection spreads unchecked:
1. Sepsis
Sepsis occurs when the body’s immune system overreacts to the infection, damaging its tissues and organs. If untreated, it can lead to septic shock and multiple organ failure.
Symptoms of Sepsis:
- Extremely high or low body temperature
- Rapid heart rate
- Confusion or dizziness
- Shortness of breath
2. Ludwig’s Angina
This is a severe skin infection in the neck and the area beneath the tongue. Ludwig’s Angina can obstruct the airways, making breathing difficult.
Symptoms of Ludwig’s Angina:
- Swelling under the chin or jaw
- Redness in the neck
- Difficulty swallowing or speaking
3. Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis
If the infection spreads to the brain, it can cause cavernous sinus thrombosis—a blood clot in a vein at the base of the brain.
Symptoms of Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis:
- Severe headache
- Vision problems or bulging eyes
- High fever
- Paralysis of eye muscles
Early Warning Signs That Shouldn’t Be Ignored
Facing a tooth infection? The earlier you act, the better. Seek immediate medical or dental care if you experience any of these symptoms:
- Persistent, throbbing toothache
- Swelling around the face or jaw
- Fever and chills
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing
- Pus draining from the tooth or gums
Ignoring these warning signs may allow the infection to worsen, requiring invasive treatments like root canals, surgery, or hospitalization.
What to Do If You Suspect a Tooth Infection
If you’re dealing with any symptoms of a potential tooth infection, take the following steps immediately:
- Schedule a Dentist Appointment: Seek professional dental care. A dentist can drain the abscess, prescribe antibiotics, and treat the root cause effectively.
- Take Prescribed Antibiotics: Completing a course of antibiotics helps control the spread of infection. However, these medications don’t replace dental intervention.
- Avoid DIY Solutions: Over-the-counter painkillers or saltwater rinses may alleviate pain but won’t resolve the infection.
Preventing Tooth Infections
The best cure is prevention. Keep your teeth and gums healthy by incorporating these habits into your daily routine:
- Brush twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles.
- Visit your dentist every six months for check-ups and cleanings.
- Avoid sugary foods or drinks that contribute to tooth decay.
FAQ
1. Can a Tooth Infection Go Away on Its Own?
No. Without treatment, a tooth infection will not resolve and can worsen over time. It’s crucial to seek dental care promptly.
2. How Quickly Can a Tooth Infection Kill You?
If the infection spreads to critical areas like the brain or bloodstream, death can occur in one to three days without treatment.
3. Are Tooth Infection Deaths Common?
Thanks to modern antibiotics and dental care, deaths from tooth infections are rare but still possible if left untreated.
4. Does Antibiotics Alone Cure Tooth Abscesses?
Antibiotics help control the spread of bacteria but don’t remove the abscess. Professional drainage or further dental treatment is needed for a complete cure.
5. What Are the Most Common Symptoms of Tooth Infection?
Common symptoms include tooth pain, swelling, fever, and pus drainage.
Take Action to Protect Your Health
Tooth infections can escalate rapidly into serious health risks, but with modern dental care, most can be treated effectively. Ignoring an infection could result in dangerous complications—don’t underestimate the warning signs.
If you’re experiencing pain or suspect an infection, contact your dentist immediately. Early treatment will save you discomfort, money, and potentially, your life.