Introduction
Understanding how to calculate the circumference of a circle is an essential math skill that applies to everyday life and various fields, from architecture to engineering. The circumference refers to the distance around a circle—similar to the perimeter of a rectangle or square.
Whether you’re a student tackling geometry problems or a professional working with circular designs, knowing how to find the circumference of a circle is a valuable skill. This guide will walk you through the formulas, practical examples, and tips to make calculating the circumference easy and straightforward.
By the end of this article, you’ll not only learn how to calculate the circumference using two simple formulas, but you’ll also understand when and how to apply them in real-world scenarios.
What is the Circumference of a Circle?
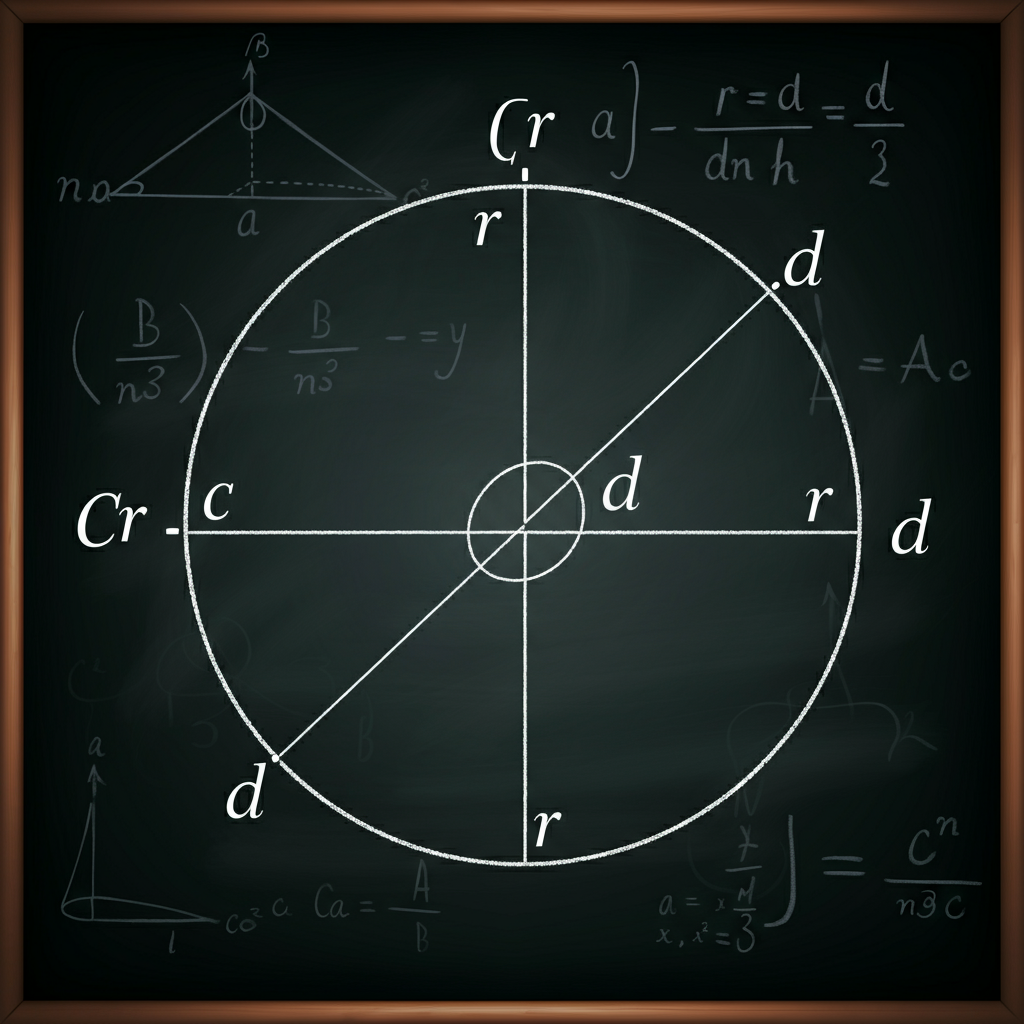
The circumference is essentially the “perimeter” of a circle—it’s the total distance you’d cover if you walked around the edge of the circle.
To find the circumference, you’ll only need one critical measurement—either the radius or the diameter—and to know the constant π (pi).
- Radius (r): The distance from the center of the circle to any point on its edge.
- Diameter (d): The circumference of the circle measured from its center. The diameter is always twice the radius of a circle.
- Pi (π): A constant approximately equal to 3.14159 (or simply 3.14 for easier calculations).
With these measurements, you can calculate the circumference using one of two primary formulas.
The Two Key Formulas to Find Circumference
- If you know the radius (r):
-
- Circumference (C) = 2 × π × r
- If you know the diameter (d):
-
- Circumference (C) = π × d
Both formulas are equally valid and interchangeable depending on whether you’re provided with the radius or diameter of the circle.
Formulas in Action: Step-by-Step Examples
Here’s how to apply the formulas with real-world examples.
Example 1: Using the Radius
Imagine you’re designing a circular garden, and you know the radius is 4 meters.
- Formula to apply: C = 2 × π × r
- Substitute the known values into the formula:
-
- C = 2 × 3.14159 × 4
- Solve the equation:
-
- C ≈ 25.13 meters
This means you’ll need about 25.13 meters of fencing to enclose your garden.
Example 2: Using the Diameter
Suppose you have a circular pizza with a diameter of 12 inches, and you want to know the circumference.
- Formula to apply: C = π × d
- Substitute the known values into the formula:
-
- C = 3.14159 × 12
- Solve the equation:
-
- C ≈ 37.7 inches
The circumference of the pizza is approximately 37.7 inches, which will help if you’re measuring its box size.
Practical Applications of Circumference
Understanding a circle’s circumference can be surprisingly useful in both everyday life and professional scenarios. Here are a few examples:
- Architecture: Calculating the circumference of cylindrical or circular structures.
- Car Tires: Determining the distance covered per rotation of a car’s tire.
- Sports: Measuring the perimeter of round objects like a cricket pitch or the basketball hoop.
By knowing how to calculate the circumference, you can make precise measurements that lead to better project outcomes or simply solve practical problems.
Common Questions about Circumference
Why is Pi (π) Important?
Pi (π) is a mathematical constant representing the ratio of a circle’s circumference to its diameter. Its value remains consistent across all circles, making it essential for any calculation involving circles. While the exact value of π is infinite, we simplify it to 3.14159 or 3.14 for convenience in calculations.
How is Circumference Useful in Geometry?
The circumference helps determine measurements in many geometry problems, like finding the area of a circle, calculating arc lengths, or assessing circular motion.
Tips for Finding the Circumference of a Circle
1. Double-Check Your Measurements
Ensure accuracy in your radius or diameter measurement. Mistakes in the initial measurement can throw off the entire calculation.
2. Use a Calculator
Since π involves many decimal places, using a calculator can save time and improve accuracy, especially for more complex calculations.
3. When in Doubt, Round Consistently
If you’re estimating, stick to a consistent approximation of π (such as 3.14) for cohesive results.
4. Understand When to Use Each Formula
- Use C = 2 × π × r when working with the radius.
- Use C = π × d when the diameter is provided directly.
FAQ Section
How do I calculate the circumference without π?
You cannot accurately calculate the circumference of a circle without using π. However, using approximations like 3.14 for π will give near-exact results.
What happens if I only have part of the circle?
If you have an arc or part of a circle, you can calculate its arc length using a fraction of the circumference. This involves additional formulas where you’ll need the circle’s central angle.
Can I find the circumference of irregular shapes?
No. The circumference formula (C = 2πr or C = πd) only applies to perfect circles. For irregular shapes, you would calculate the perimeter instead.
What’s the difference between diameter and radius?
The diameter is twice the radius. Think of the radius as half the length of the diameter.
Why Knowing Circumference is Key
Mastering “how to find the circumference of a circle” equips you with an essential skill, whether for academic purposes or real-world applications. By understanding the core formulas and practicing examples, you can confidently solve related problems and even apply these skills in unexpected scenarios.